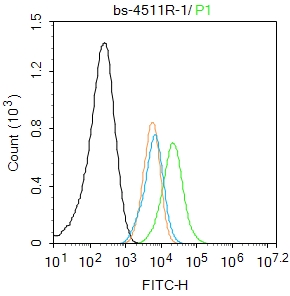
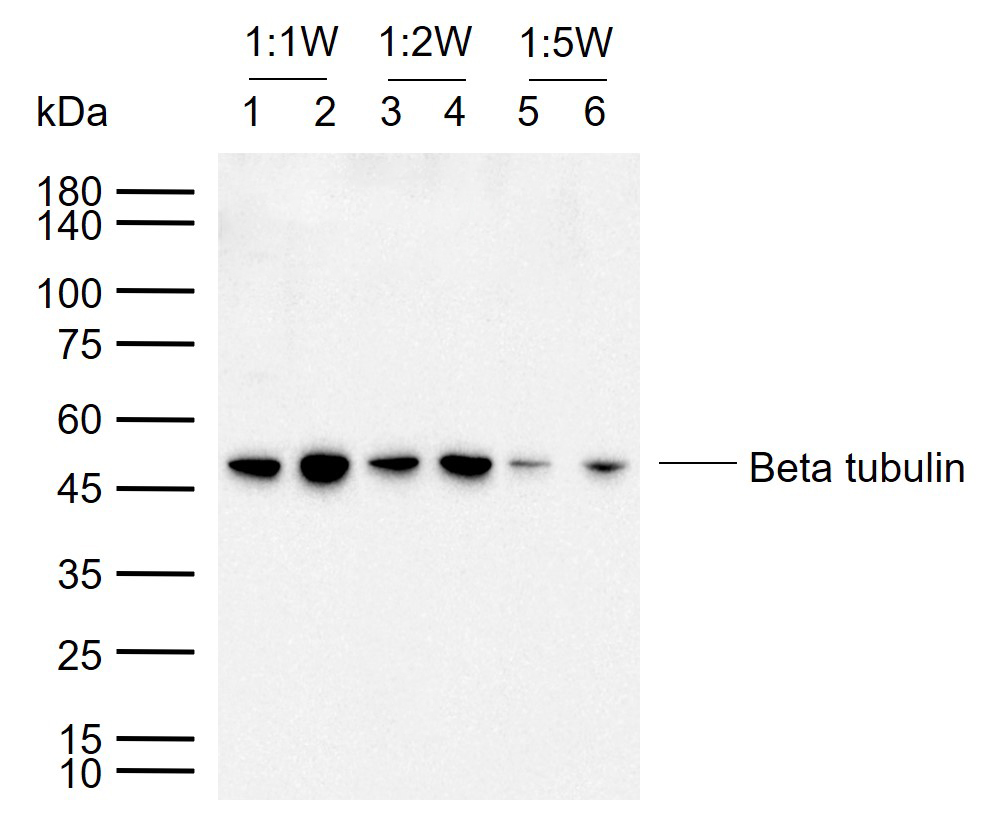
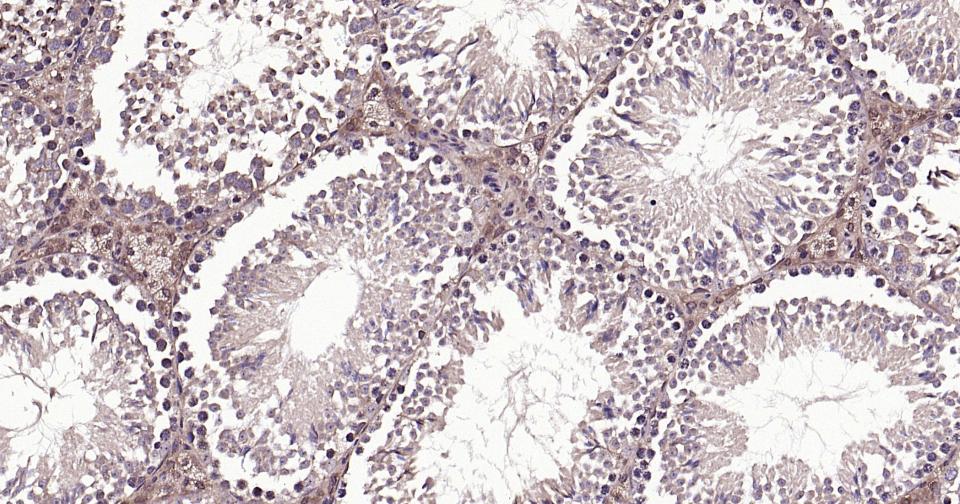
Beta tubulin Rabbit pAb, Loading Control
Beta tubulin Rabbit pAb, Loading Control
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 1
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P07437 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 49671 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human tubulin Beta |
| Epitope Specificity | 61-160/444 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cytoplasmic, cytoskeleton. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the tubulin family. |
| SUBUNIT | Dimer of alpha and beta chains. May interact with RNABP10. Interacts with PIFO. Interacts with MX1. |
| Post-translational modifications | Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated. This modification occurs exclusively on glutamate residues and results in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group. Also monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into axonemes (cilia and flagella) whereas glutamylation is prevalent in neuronal cells, centrioles, axonemes, and the mitotic spindle. Both modifications can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally. The precise function of such modifications is still unclear but they regulate the assembly and dynamics of axonemal microtubules (Probable). |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a beta tubulin protein. This protein forms a dimer with alpha tubulin and acts as a structural component of microtubules. Mutations in this gene cause cortical dysplasia, complex, with other brain malformations 6. Alternative splicing results in multiple splice variants. There are multiple pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014] |
| Gene ID | 203068 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Tubulin beta chain, Tubulin beta-5 chain, TUBB, TUBB5 |
| Target/Specificity | Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels in spleen, thymus and immature brain. |
| Dilution | WB=1:10000-100000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,Flow-Cyt=1ug/Test |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | TUBB |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | TUBB5 |
| Function | Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed with highest levels in spleen, thymus and immature brain. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes a beta tubulin protein. This protein forms a dimer with alpha tubulin and acts as a structural component of microtubules. Mutations in this gene cause cortical dysplasia, complex, with other brain malformations 6. Alternative splicing results in multiple splice variants. There are multiple pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014]
REFERENCES
Lee M.G.-S.,et al.Cell 33:477-487(1983).
Hall J.L.,et al.Mol. Cell. Biol. 3:854-862(1983).
Crabtree D.V.,et al.Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9:1967-1976(2001).
Yu W.,et al.Submitted (JUN-1998) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Shiina S.,et al.Submitted (SEP-1999) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。