Podoplanin Rabbit pAb
Podoplanin Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
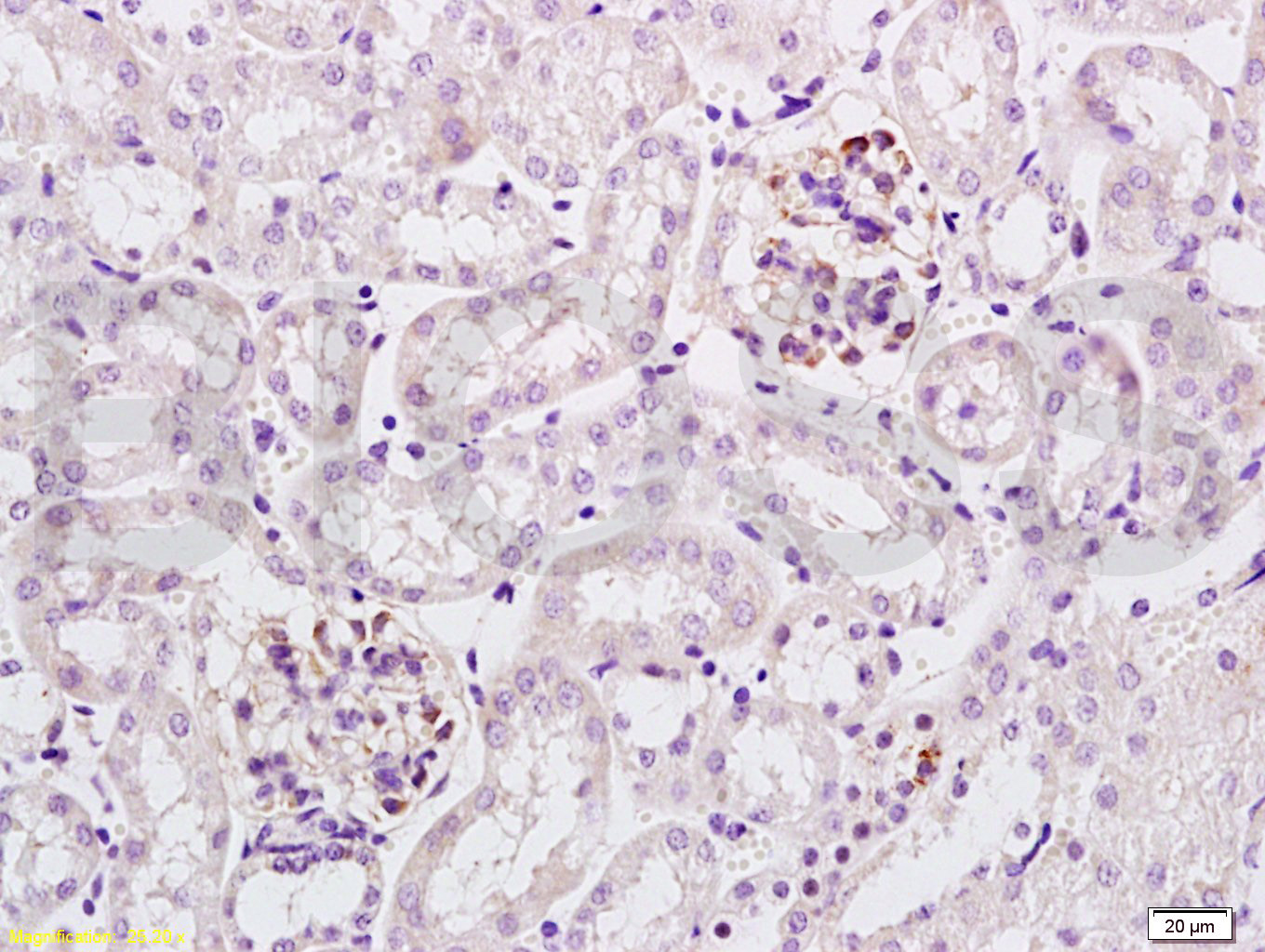
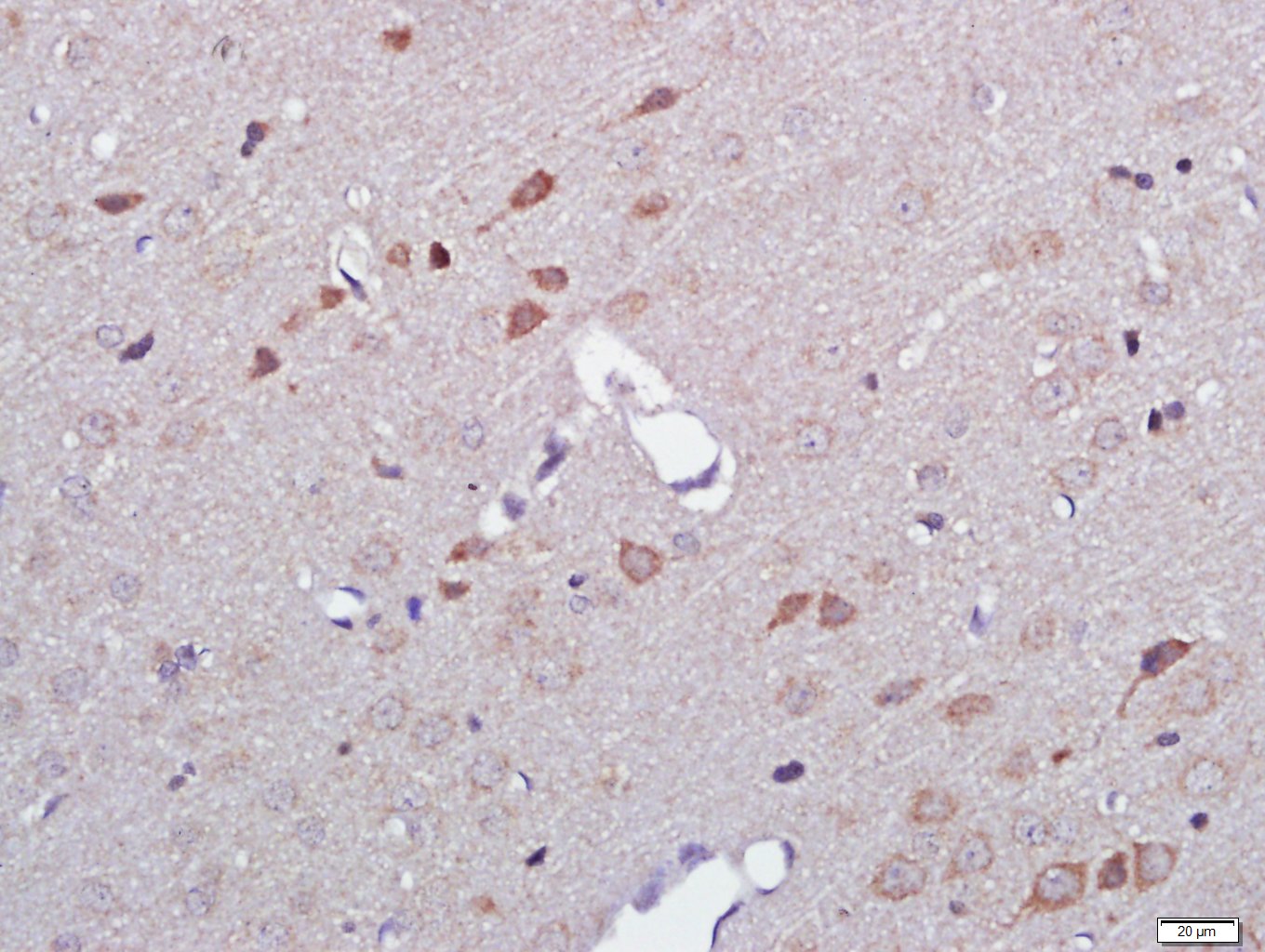
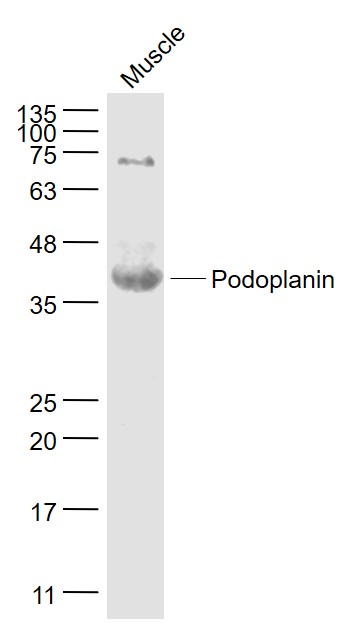
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q62011 |
| Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 18233 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from mouse Podoplanin |
| Epitope Specificity | 91-166/166 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, filopodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, microvillus membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, ruffle membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Localized to actin-rich microvilli and plasma membrane projections such as filopodia, lamellipodia and ruffles. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the podoplanin family. |
| Post-translational modifications | Extensively O-glycosylated. Contains sialic acid residues. O-glycosylation is necessary for platelet aggregation activity. The N-terminus is blocked. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | This gene encodes a type-I integral membrane glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The physiological function of this protein may be related to its mucin-type character. The homologous protein in other species has been described as a differentiation antigen and influenza-virus receptor. The specific function of this protein has not been determined but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Gene ID | 14726 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Podoplanin, Pdpn {ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:103098} |
| Target/Specificity | Highly expressed in placenta, lung, skeletal muscle and brain. Weakly expressed in brain, kidney and liver. In placenta, expressed on the apical plasma membrane of endothelium. In lung, expressed in alveolar epithelium. Up-regulated in colorectal tumors and expressed in 25% of early oral squamous cell carcinomas. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | Pdpn {ECO:0000312|MGI:MGI:103098} |
|---|---|
| Function | Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. During development plays a role in blood and lymphatic vessels separation by binding CLEC1B, triggering CLEC1B activation in platelets and leading to platelet activation and/or aggregation (PubMed:14522983, PubMed:15231832, PubMed:17616532, PubMed:20110424). Interaction with CD9, on the contrary, attenuates platelet aggregation and pulmonary metastasis induced by PDPN. Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. Through MSN or EZR interaction promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leading to ERZ phosphorylation and triggering RHOA activation leading to cell migration increase and invasiveness. Interaction with CD44 promotes directional cell migration in epithelial and tumor cells (By similarity). In lymph nodes (LNs), controls fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and contraction of the actomyosin by maintaining ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation through association with unknown transmembrane proteins. Engagement of CLEC1B by PDPN promotes FRCs relaxation by blocking lateral membrane interactions leading to reduction of ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation (PubMed:25347465). Through binding with LGALS8 may participate in connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix (By similarity). In keratinocytes, induces changes in cell morphology showing an elongated shape, numerous membrane protrusions, major reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, increased motility and decreased cell adhesion (PubMed:10574709). Controls invadopodia stability and maturation leading to efficient degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in tumor cells through modulation of RHOC activity in order to activate ROCK1/ROCK2 and LIMK1/LIMK2 and inactivation of CFL1 (By similarity). Required for normal lung cell proliferation and alveolus formation at birth (PubMed:12654292). Does not function as a water channel or as a regulator of aquaporin-type water channels (By similarity). Does not have any effect on folic acid or amino acid transport (PubMed:12032185). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, filopodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, microvillus membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, ruffle membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane raft {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Basolateral cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Cell projection, invadopodium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Note=Localized to actin-rich microvilli and plasma membrane projections such as filopodia, lamellipodia and ruffles (PubMed:10574709). Association to the lipid rafts is required for PDPN-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) Colocalizes with CD9 in tetraspanin microdomains. Localized at invadopodium adhesion rings in tumor cell. Association to the lipid rafts is essential for PDPN recruitment to invadopodia and ECM degradation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574709} |
| Tissue Location | Detected at high levels in lung and brain, at lower levels in kidney, stomach, liver, spleen and esophagus, and not detected in skin and small intestine. Expressed in epithelial cells of choroid plexus, ependyma, glomerulus and alveolus, in mesothelial cells and in endothelia of lymphatic vessels. Also expressed in stromal cells of peripheral lymphoid tissue and thymic epithelial cells. Detected in carcinoma cell lines and cultured fibroblasts. Expressed at higher levels in colon carcinomas than in normal colon tissue |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。