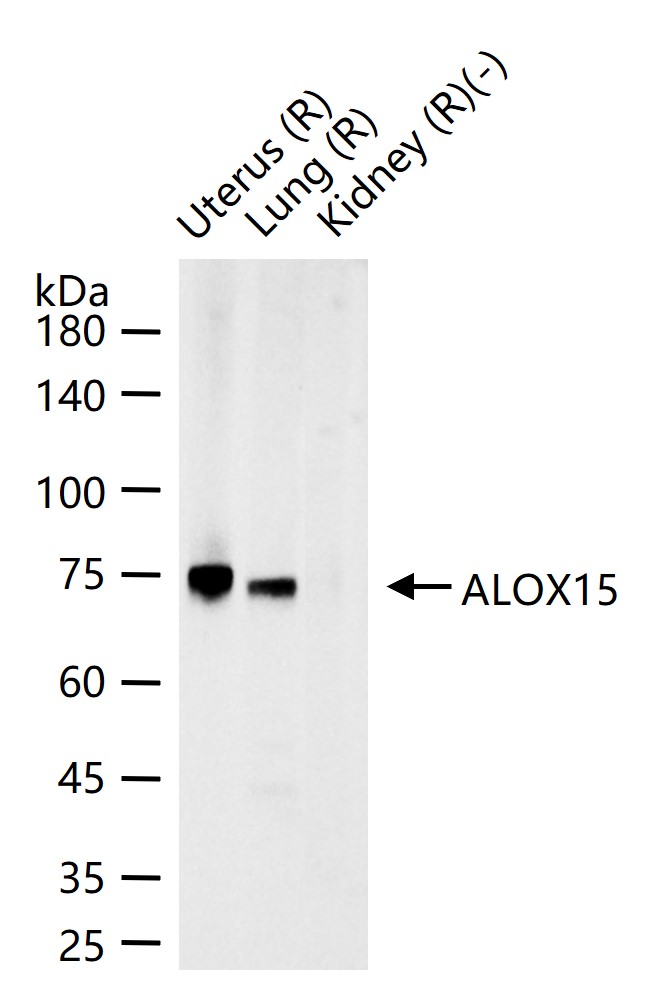
ALOX15 Rabbit pAb
ALOX15 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 75 KDa |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from mouse 15 Lipoxygenase 1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 111-210/663 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Cytoplasm. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the lipoxygenase family. Contains 1 lipoxygenase domain. Contains 1 PLAT domain. |
| SUBUNIT | Homotetramer. Can also form heterotetramers with RYR2. Interacts with CALM; CALM with bound calcium inhibits the RYR1 channel activity. Interacts with S100A1. Interacts with FKBP1A; this stabilizes the closed conformation of the channel. Interacts with CACNA1S; interaction with CACNA1S is important for activation of the RYR1 channel. Interacts with CACNB1. Interacts with TRDN and ASPH; these interactions stimulate RYR1 channel activity (By similarity). Identified in a complex composed of RYR1, PDE4D, PKA, FKBP1A and protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Repeated very high-level exercise decreases interaction with PDE4D and protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). |
| Post-translational modifications | Channel activity is modulated by phosphorylation. Phosphorylation at Ser-2843 may increase channel activity. Repeated very high-level exercise increases phosphorylation at Ser-2843. Activated by reversible S-nitrosylation. Repeated very high-level exercise increases S-nitrosylation. |
| DISEASE | Malignant hyperthermia 1 (MHS1) [MIM:145600]: Autosomal dominant pharmacogenetic disorder of skeletal muscle and is one of the main causes of death due to anesthesia. In susceptible people, an MH episode can be triggered by all commonly used inhalational anesthetics such as halothane and by depolarizing muscle relaxants such as succinylcholine. The clinical features of the myopathy are hyperthermia, accelerated muscle metabolism, contractures, metabolic acidosis, tachycardia and death, if not treated with the postsynaptic muscle relaxant, dantrolene. Susceptibility to MH can be determined with the 'in vitro' contracture test (IVCT): observing the magnitude of contractures induced in strips of muscle tissue by caffeine alone and halothane alone. Patients with normal response are MH normal (MHN), those with abnormal response to caffeine alone or halothane alone are MH equivocal (MHE(C) and MHE(H) respectively). Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Central core disease of muscle (CCD) [MIM:117000]: Autosomal dominant congenital myopathy, but a severe autosomal recessive form also exists. Both clinical and histological variability is observed. Affected individuals typically display hypotonia and proximal muscle weakness in infancy, leading to the delay of motor milestones. The clinical course of the disorder is usually slow or nonprogressive in adulthood, and the severity of the symptoms may vary from normal to significant muscle weakness. Microscopic examination of CCD-affected skeletal muscle reveals a predominance of type I fibers containing amorphous-looking areas (cores) that do not stain with oxidative and phosphorylase histochemical techniques. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Multiminicore disease with external ophthalmoplegia (MMDO) [MIM:255320]: Clinically heterogeneous neuromuscular disorder. General features include neonatal hypotonia, delayed motor development, and generalized muscle weakness and amyotrophy, which may progress slowly or remain stable. Muscle biopsy shows multiple, poorly circumscribed, short areas of sarcomere disorganization and mitochondria depletion (areas termed minicores) in most muscle fibers. Typically, no dystrophic signs, such as muscle fiber necrosis or regeneration or significant endomysial fibrosis, are present in multiminicore disease. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) [MIM:255310]: Genetically heterogeneous disorder in which there is relative hypotrophy of type 1 muscle fibers compared to type 2 fibers on skeletal muscle biopsy. However, these findings are not specific and can be found in many different myopathic and neuropathic conditions. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry. Note=Defects in RYR1 may be a cause of Samaritan myopathy, a congenital myopathy with benign course. Patients display severe hypotonia and respiratory distress at birth. Unlike other congenital myopathies, the health status constantly improves and patients are minimally affected at adulthood. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Lipoxygenases are a family of enzymes which dioxygenate unsaturated fatty acids, thus initiating lipoperoxidation of membranes and synthesis of signaling molecules, as well as inducing structural and metabolic changes in the cell. The Lox enzymes in mammals include 12-LO and 15-LO, which are classified with respect to their positional specificity of the deoxygenation of their most common substrate, arachidonic acid. The metabolism of arachidonic acid leads to the generation of biologically active metabolites that have been implicated in cell growth and proliferation, as well as survival and apoptosis. 15-Lipoxygenase (15-LO) acts in physiological membrane remodeling and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, inflammation, and carcinogenesis. It is highly regulated and expressed in a tissue- and cell-type-specific fashion. IL-4 and IL-13 play important roles in transactivating the 15-LO gene. Overexpression of 15-LO type 1 in prostate cancer contributes to the cancer progression by regulating IGF-1R expression and activation. |
| Target/Specificity | Skeletal muscle and brain (cerebellum and hippocampus). |
|---|---|
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。