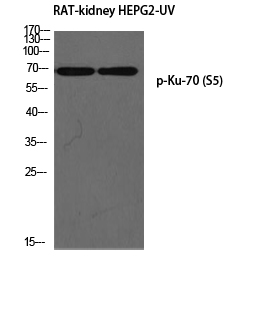
Ku-70 (phospho Ser5) Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P12956 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 69843 Da |
| Gene ID | 2547 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | XRCC6; G22P1; X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6; 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase Ku70; 5'-dRP lyase Ku70; 70 kDa subunit of Ku antigen; ATP-dependent DNA helicase 2 subunit 1; ATP-dependent DNA helicase II 70 kDa subunit; CTC box- |
| Dilution | WB~~Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. IHC-P~~1:50~200 IF~~1:50~200 ICC~~N/A E~~N/A |
| Format | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage Conditions | -20℃ |
| Name | XRCC6 (HGNC:4055) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | G22P1 |
| Function | DNA-binding protein critical for the DNA damage response, specifically in repairing double-strand breaks (DSBs) via the classical non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway. It forms a heterodimer with XRCC5 (Ku80), creating the Ku70:Ku80 heterodimer (Ku complex), which serves as a DNA end-binding complex. It primarily binds DSBs and recruits essential repair factors, assembling the core long-range NHEJ complex to facilitate the alignment and ligation of broken DNA ends (PubMed:11493912, PubMed:20493174, PubMed:33854234, PubMed:34352203, PubMed:9742108). This pathway ensures the rapid repair of cytotoxic and mutagenic DSBs and contributes to the generation of diversity in T-cell receptors and antibodies through mechanisms such as V(D)J recombination (PubMed:9742108). Likely acts as a 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase (5'-dRP lyase), catalyzing the beta-elimination of the 5'-deoxyribose- 5-phosphate at abasic sites near DSBs. This activity cleans the termini of abasic sites, a common form of nucleotide damage, preparing broken ends for ligation (PubMed:20383123). It may also possess 3'-5' DNA helicase activity, although this has not been confirmed in vivo, and its physiological significance remains unclear (PubMed:7957065). Beyond DNA repair, the protein contributes to telomere maintenance (PubMed:29490055). It is also implicated in transcriptional regulation, acting as a cofactor for various transcription factors (PubMed:12145306, PubMed:8621488). It plays a role in the regulation of DNA virus-mediated innate immune response by assembling into the HDP- RNP complex, a complex that serves as a platform for IRF3 phosphorylation and subsequent innate immune response activation through the cGAS-STING pathway (PubMed:28712728). Can also bind RNAs and recruits PRKDC to a wide range of cellular RNAs, including the U3 small nucleolar RNA, playing a role in the biogenesis of ribosomal RNAs (PubMed:32103174). Additionally, it negatively regulates apoptosis by interacting with BAX, sequestering it from the mitochondria, and may possess deubiquitination activity targeting BAX (PubMed:15023334, PubMed:18362350, PubMed:35545041). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome. Cytoplasm. Note=When trimethylated, localizes in the cytoplasm. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Single-stranded DNA-dependent ATP-dependent helicase. Has a role in chromosome translocation. The DNA helicase II complex binds preferentially to fork-like ends of double-stranded DNA in a cell cycle-dependent manner. It works in the 3'-5' direction. Binding to DNA may be mediated by XRCC6. Involved in DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination. The XRCC5/6 dimer acts as regulatory subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase complex DNA-PK by increasing the affinity of the catalytic subunit PRKDC to DNA by 100-fold. The XRCC5/6 dimer is probably involved in stabilizing broken DNA ends and bringing them together. The assembly of the DNA-PK complex to DNA ends is required for the NHEJ ligation step. Required for osteocalcin gene expression. Probably also acts as a 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase (5'-dRP lyase), by catalyzing the beta-elimination of the 5' deoxyribose- 5-phosphate at an abasic site near double-strand breaks. 5'-dRP lyase activity allows to 'clean' the termini of abasic sites, a class of nucleotide damage commonly associated with strand breaks, before such broken ends can be joined. The XRCC5/6 dimer together with APEX1 acts as a negative regulator of transcription. Plays a role in the regulation of DNA virus-mediated innate immune response by assembling into the HDP-RNP complex, a complex that serves as a platform for IRF3 phosphorylation and subsequent innate immune response activation through the cGAS-STING pathway.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。