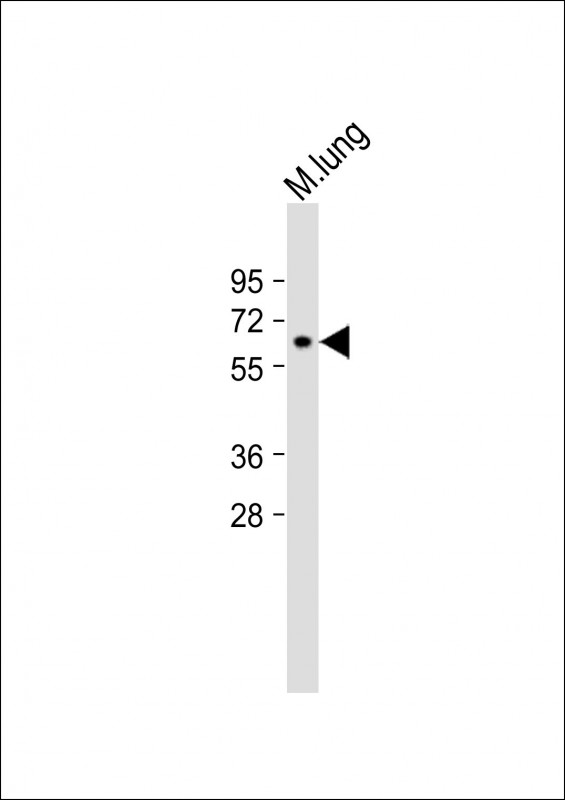
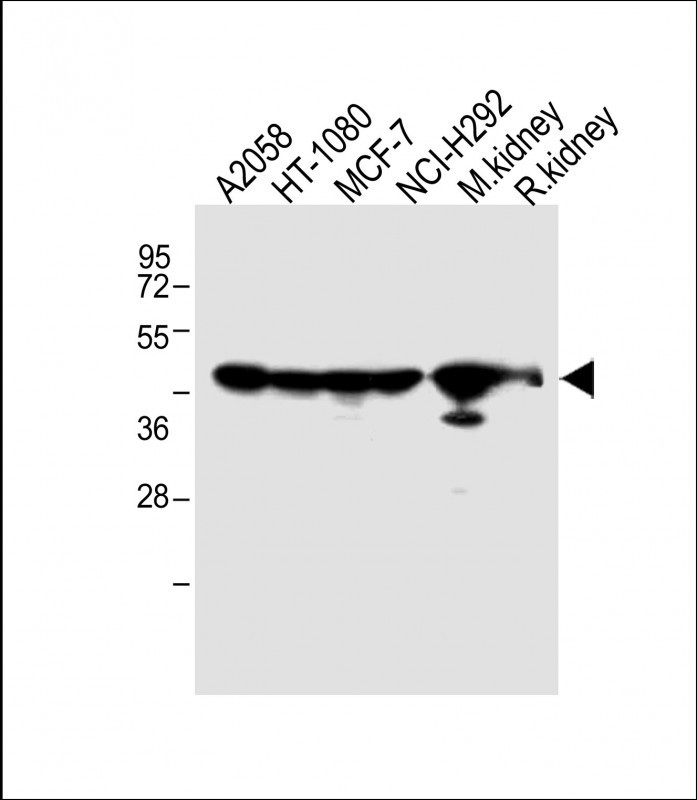
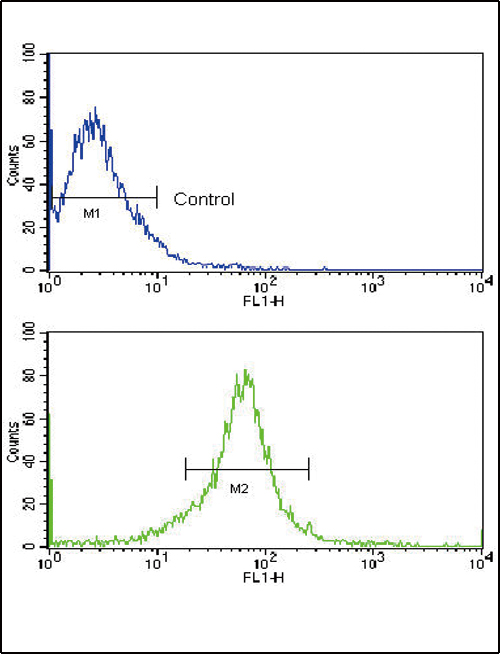
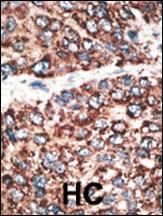
MMP14 Antibody (N-term)
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 3
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, FC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P50281 |
| Other Accession | Q10739, Q9XT90, P53690, Q9GLE4, NP_004986 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Predicted | Mouse, Rat, Pig, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 65894 Da |
| Antigen Region | 145-174 aa |
| Gene ID | 4323 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Matrix metalloproteinase-14, MMP-14, MMP-X1, Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase 1, MT-MMP 1, MTMMP1, Membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase, MT1-MMP, MT1MMP, MMP14 |
| Target/Specificity | This MMP14 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 145-174 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human MMP14. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 FC~~1:10~50 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | MMP14 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MMP14 |
|---|---|
| Function | Endopeptidase that degrades various components of the extracellular matrix such as collagen (PubMed:8015608). Essential for pericellular collagenolysis and modeling of skeletal and extraskeletal connective tissues during development (By similarity). Activates progelatinase A/MMP2, thereby acting as a positive regulator of cell growth and migration (PubMed:22065321, PubMed:8015608). Involved in the formation of the fibrovascular tissues in association with pro-MMP2 (PubMed:12714657, PubMed:22065321). May be involved in actin cytoskeleton reorganization by cleaving PTK7 (PubMed:20837484). Acts as a regulator of Notch signaling by mediating cleavage and inhibition of DLL1 (PubMed:21572390). Cleaves ADGRB1 to release vasculostatin-40 which inhibits angiogenesis (PubMed:22330140). Acts as a negative regulator of the GDF15-GFRAL aversive response by mediating cleavage and inactivation of GFRAL (PubMed:35177851). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Melanosome. Cytoplasm Note=Identified by mass spectrometry in melanosome fractions from stage I to stage IV (PubMed:17081065). Forms a complex with BST2 and localizes to the cytoplasm (PubMed:17081065) |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in stromal cells of colon, breast, and head and neck. Expressed in lung tumors. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. MMP14 seems to specifically activate progelatinase A, and may thus trigger invasion by tumor cells by activating progelatinase A on the tumor cell surface. Expression is significant in stromal cells of colon, breast, and head and neck.
REFERENCES
Will, H., et al., Eur. J. Biochem. 231(3):602-608 (1995).
Takino, T., et al., Gene 155(2):293-298 (1995).
Okada, A., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92(7):2730-2734 (1995).
Sato, H., et al., Nature 370(6484):61-65 (1994).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。