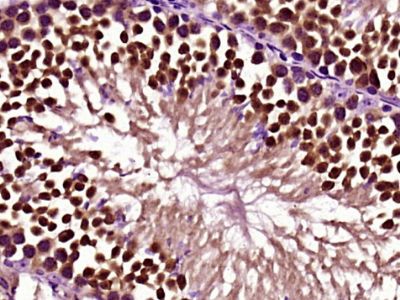
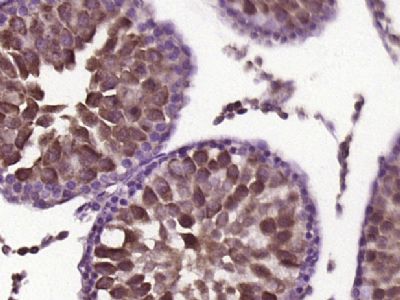
Gli3 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P10071 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 169863 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Gli3 |
| Epitope Specificity | 481-570/1580 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell projection |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the GLI C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family. Contains 5 C2H2-type zinc fingers. |
| SUBUNIT | The full-length GLI3 form (GLI3FL) interacts with SUFU and this interaction regulates the formation of either repressor or activator forms of GLI3. Its association with SUFU is regulated by Hh signaling and dissociation of the SUFU-GLI3 interaction requires the presence of the ciliary motor KIF3A (By similarity). Interacts with KIF7. The activator form of GLI3 (GLI3A) but not the repressor form (GLI3R) can interact with TRPS1. The phosphorylated form interacts with BTRC. Interacts with ZIC1. Interacts with ZIC3 (via C2H2-type domains 3, 4 and 5); the interaction enhances its transcriptional activity. |
| Post-translational modifications | Phosphorylated on multiple sites by protein kinase A (PKA) and phosphorylation by PKA primes further phosphorylation by CK1 and GSK3. Phosphorylation is essential for its proteolytic processing. Transcriptional repressor GLI3R, a C-terminally truncated form, is generated from the full-length GLI3 protein (GLI3FL/GLI3-190) through proteolytic processing. This process requires PKA-primed phosphorylation of GLI3, ubiquitination of GLI3 and the presence of BTRC. GLI3FL is complexed with SUFU in the cytoplasm and is maintained in a neutral state. Without the Hh signal, the SUFU-GLI3 complex is recruited to cilia, leading to the efficient processing of GLI3FL into GLI3R. GLI3R formation leads to its dissociation from SUFU, allowing it to translocate into the nucleus, and repress Hh target genes. When Hh signaling is initiated, SUFU dissociates from GLI3FL and this has two consequences. First, GLI3R production is halted. Second, free GLI3FL translocates to the nucleus, where it is phosphorylated, destabilized, and converted to a transcriptional activator (GLI3A). Phosphorylated in vitro by ULK3. |
| DISEASE | Defects in GLI3 are the cause of Greig cephalo-poly-syndactyly syndrome (GCPS) [MIM:175700]. GCPS is an autosomal dominant disorder affecting limb and craniofacial development. It is characterized by pre- and postaxial polydactyly, syndactyly of fingers and toes, macrocephaly and hypertelorism. Defects in GLI3 are a cause of Pallister-Hall syndrome (PHS) [MIM:146510]. PHS is characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations. It mainly associates central or postaxial polydactyly, syndactyly, and hypothalamic hamartoma. Malformations are frequent in the viscera, e.g. anal atresia, bifid uvula, congenital heart malformations, pulmonary or renal dysplasia. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. Defects in GLI3 are a cause of type A1/B postaxial polydactyly (PAPA1/PAPB) [MIM:174200, 603596]. PAPA in humans is an autosomal dominant trait characterized by an extra digit in the ulnar and/or fibular side of the upper and/or lower extremities. The extra digit is well formed and articulates with the fifth, or extra, metacarpal/metatarsal, and thus it is usually functional. Defects in GLI3 are a cause of polydactyly preaxial type 4 (POP4) [MIM:174700]. Polydactyly preaxial type 4 (i.e., polydactyly on the radial/tibial side of the hand/foot) covers a heterogeneous group of entities. In preaxial polydactyly type IV, the thumb shows only the mildest degree of duplication, and syndactyly of various degrees affects fingers 3 and 4. Defects in GLI3 are the cause of acrocallosal syndrome (ACS) [MIM:200990]; also abbreviated ACLS. ACS is characterized by postaxial polydactyly, hallux duplication, macrocephaly, and absence of the corpus callosum, usually with severe developmental delay. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | It has long been known that the overexpression of either Wnt-1 or the GLI proteins results in cancer; however, the molecular basis for this transformation was poorly understood. The Wnt-1 and GLI proteins have now been placed in a signaling cascade downstream of the mammalian homologs of the Drosophila hedgehog and patched proteins. The Drosophila segment polarity gene hedgehog (hh) encodes a secreted protein that appears to function in embryonic and imaginal disc patterning. The ptc gene, also identified as a Drosophila segment polarity gene, encodes the transmembrane protein patched, the expression of which is precisely regulated during embryonic development. Hedgehog has been shown to enhance the expression of the Wnt family of proteins through a signaling cascade involving the GLI transcription factors, while patched functions as a repressor opposing the effects of hedgehog. Mutations in the ptc gene, which result in unregulated hedgehog signaling, have been correlated with the most common type of cancer, basal cell carcinoma, which affects 750,000 individuals annually in the United States alone. |
| Gene ID | 2737 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Transcriptional activator GLI3, GLI3 form of 190 kDa, GLI3-190, GLI3 full-length protein, GLI3FL, Transcriptional repressor GLI3R, GLI3 C-terminally truncated form, GLI3 form of 83 kDa, GLI3-83, GLI3 |
| Target/Specificity | Is expressed in a wide variety of normal adult tissues, including lung, colon, spleen, placenta, testis, and myometrium. |
| Dilution | IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | GLI3 |
|---|---|
| Function | Has a dual function as a transcriptional activator and a repressor of the sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway, and plays a role in limb development. The full-length GLI3 form (GLI3FL) after phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, acts as an activator (GLI3A) while GLI3R, its C-terminally truncated form, acts as a repressor. A proper balance between the GLI3 activator and the repressor GLI3R, rather than the repressor gradient itself or the activator/repressor ratio gradient, specifies limb digit number and identity. In concert with TRPS1, plays a role in regulating the size of the zone of distal chondrocytes, in restricting the zone of PTHLH expression in distal cells and in activating chondrocyte proliferation. Binds to the minimal GLI- consensus sequence 5'-GGGTGGTC-3'. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell projection, cilium. Note=GLI3FL is localized predominantly in the cytoplasm while GLI3R resides mainly in the nucleus. Ciliary accumulation requires the presence of KIF7 and SMO. Translocation to the nucleus is promoted by interaction with ZIC1 |
| Tissue Location | Is expressed in a wide variety of normal adult tissues, including lung, colon, spleen, placenta, testis, and myometrium |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,500.00
Cat# AP54547























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。