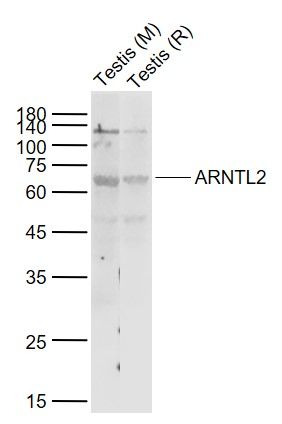
ARNTL2 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8WYA1 |
| Reactivity | Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 70887 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human ARNTL2 |
| Epitope Specificity | 381-480/636 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Nuclear |
| SIMILARITY | Contains 1 bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) domain. Contains 1 PAC (PAS-associated C-terminal) domain. Contains 2 PAS (PER-ARNT-SIM) domains. |
| SUBUNIT | Component of the circadian core oscillator, which includes the CRY proteins, CLOCK, or NPAS2, ARNTL or ARNTL2, CSNK1D and/or CSNK1E, TIMELESS and the PER proteins. Interacts directly with CLOCK to form the ARNTL2-CLOCK transactivator. Can form heterodimers or homodimers which interact directly with CLOCK to form the transcription activator. Also interacts with NPAS2 and HIF1A. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | BMAL2 is a 636 amino acid protein that localizes to the nucleus and contains one bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) domain, one PAC (PAS-associated C-terminal) domain and two PAS (PER-ARNT-SIM) domains. Expressed at high levels in placenta and brain and at lower levels in liver, thymus, heart, lung and kidney, BMAL2 functions as a component of the circadian core oscillator, which includes a variety of proteins that work in tandem to activate the transcription of target genes. More specifically, BMAL2, when functioning as a component of the core oscillator, binds to the E-box element (3'-CACGTG-5') of target DNA, thus inducing transcription. Multiple isoforms of BMAL2 exist due to alternative splicing events. |
| Gene ID | 56938 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 2, Basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP9, Brain and muscle ARNT-like 2, CYCLE-like factor, CLIF, Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 6, bHLHe6, Member of PAS protein 9, PAS domain-containing protein 9, ARNTL2, BHLHE6, BMAL2, CLIF, MOP9, PASD9 |
| Target/Specificity | Expressed in fetal brain. Highly expressed in brain and placenta. Lower levels in heart, liver, thymus, kidney and lung. Located to endothelial cells and neuronal cells of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). Also detected in endothelial cells of the heart, lung and kidney. In the brain, specifically expressed in the thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,Flow-Cyt=2ug/test,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | BMAL2 (HGNC:18984) |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcriptional activator which forms a core component of the circadian clock. The circadian clock, an internal time-keeping system, regulates various physiological processes through the generation of approximately 24 hour circadian rhythms in gene expression, which are translated into rhythms in metabolism and behavior. It is derived from the Latin roots 'circa' (about) and 'diem' (day) and acts as an important regulator of a wide array of physiological functions including metabolism, sleep, body temperature, blood pressure, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and renal function. Consists of two major components: the central clock, residing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, and the peripheral clocks that are present in nearly every tissue and organ system. Both the central and peripheral clocks can be reset by environmental cues, also known as Zeitgebers (German for 'timegivers'). The predominant Zeitgeber for the central clock is light, which is sensed by retina and signals directly to the SCN. The central clock entrains the peripheral clocks through neuronal and hormonal signals, body temperature and feeding-related cues, aligning all clocks with the external light/dark cycle. Circadian rhythms allow an organism to achieve temporal homeostasis with its environment at the molecular level by regulating gene expression to create a peak of protein expression once every 24 hours to control when a particular physiological process is most active with respect to the solar day. Transcription and translation of core clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, BMAL1, BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1 and CRY2) plays a critical role in rhythm generation, whereas delays imposed by post- translational modifications (PTMs) are important for determining the period (tau) of the rhythms (tau refers to the period of a rhythm and is the length, in time, of one complete cycle). A diurnal rhythm is synchronized with the day/night cycle, while the ultradian and infradian rhythms have a period shorter and longer than 24 hours, respectively. Disruptions in the circadian rhythms contribute to the pathology of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndromes and aging. A transcription/translation feedback loop (TTFL) forms the core of the molecular circadian clock mechanism. Transcription factors, CLOCK or NPAS2 and BMAL1 or BMAL2, form the positive limb of the feedback loop, act in the form of a heterodimer and activate the transcription of core clock genes and clock-controlled genes (involved in key metabolic processes), harboring E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') within their promoters. The core clock genes: PER1/2/3 and CRY1/2 which are transcriptional repressors form the negative limb of the feedback loop and interact with the CLOCK|NPAS2-BMAL1|BMAL2 heterodimer inhibiting its activity and thereby negatively regulating their own expression. This heterodimer also activates nuclear receptors NR1D1/2 and RORA/B/G, which form a second feedback loop and which activate and repress BMAL1 transcription, respectively. The CLOCK-BMAL2 heterodimer activates the transcription of SERPINE1/PAI1 and BHLHE40/DEC1. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10964693} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in fetal brain. Highly expressed in brain and placenta. Lower levels in heart, liver, thymus, kidney and lung Located to endothelial cells and neuronal cells of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). Also detected in endothelial cells of the heart, lung and kidney. In the brain, specifically expressed in the thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,500.00
Cat# AP54505























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。