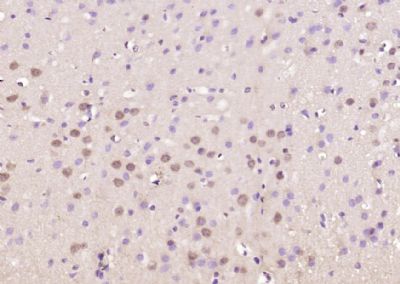
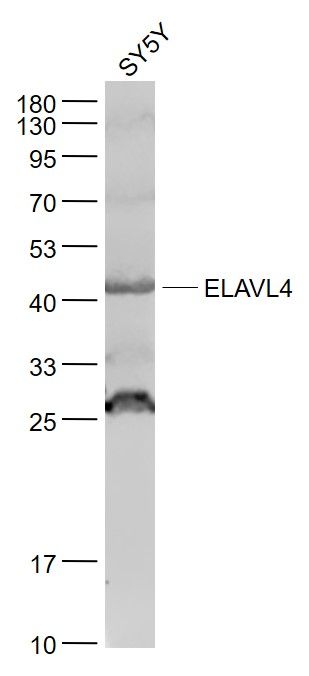
ELAVL4 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P26378 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Dog, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 42398 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human ELAVL4 |
| Epitope Specificity | 51-150/380 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Interacts with IGF2BP1. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the RRM elav family. Contains 3 RRM (RNA recognition motif) domains. |
| SUBUNIT | Component of a TAU mRNP complex, at least composed of IGF2BP1, ELAVL4 and G3BP (By similarity). |
| Post-translational modifications | Methylation at Arg-243 by CARM1 weakens protective binding to the 3'-UTR of CDKN1A mRNA and down-regulates CDKN1A protein expression, thereby maintaining cells in a proliferative state. Methylation is inhibited by NGF, which facilitates neurite outgrowth. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | The Elav-like genes encode for a family of RNA-binding proteins. Elav, a Drosophila protein and the first described member, is expressed immediately after neuroblastic differentiation into neurons and is necessary for neuronal differentiation and maintenance. Several mammalian Elav-like proteins, designated HuC, HuD and Hel-N1, are also expressed in postmitotic neurons. An additional mammalian homolog, HuR, which is also designated HuA, is ubiquitously expressed and is also overexpressed in a wide variety of tumors. Characteristically, these homologs all contain three RNA recognition motifs (RRM) and they specifically bind to AU-rich elements (ARE) in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNAs transcripts. ARE sites target mRNA for rapid degradation and thereby regulate the expression levels of genes involved in cell growth and differentiation. When Elav-like proteins associate with these ARE sites this degradation is inhibited, leading to an increased stability of the corresponding transcript. Elav proteins function within the nucleus, and they are shuttled between the nucleus and cytoplasm by a nuclear export signal, which is a regulatory feature of the Elav-like proteins as it limits their accessibility to ARE sites. |
| Gene ID | 1996 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | ELAV-like protein 4, Hu-antigen D, HuD, Paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen HuD, ELAVL4, HUD, PNEM |
| Target/Specificity | Brain. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | ELAVL4 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HUD, PNEM |
| Function | RNA-binding protein that is involved in the post- transcriptional regulation of mRNAs (PubMed:10710437, PubMed:12034726, PubMed:12468554, PubMed:17035636, PubMed:17234598, PubMed:7898713). Plays a role in the regulation of mRNA stability, alternative splicing and translation (PubMed:10710437, PubMed:12034726, PubMed:12468554, PubMed:17035636, PubMed:17234598, PubMed:7898713). Binds to AU-rich element (ARE) sequences in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs, including GAP43, VEGF, FOS, CDKN1A and ACHE mRNA (PubMed:10710437, PubMed:12034726, PubMed:12468554, PubMed:7898713). Many of the target mRNAs are coding for RNA-binding proteins, transcription factors and proteins involved in RNA processing and/or neuronal development and function (By similarity). By binding to the mRNA 3'UTR, decreases mRNA deadenylation and thereby contributes to the stabilization of mRNA molecules and their protection from decay (PubMed:12034726). Also binds to the polyadenylated (poly(A)) tail in the 3'UTR of mRNA, thereby increasing its affinity for mRNA binding (PubMed:12034726). Mainly plays a role in neuron-specific RNA processing by stabilization of mRNAs such as GAP43, ACHE and mRNAs of other neuronal proteins, thereby contributing to the differentiation of neural progenitor cells, nervous system development, learning and memory mechanisms (PubMed:12034726, PubMed:12468554, PubMed:17234598, PubMed:18218628). Involved in the negative regulation of the proliferative activity of neuronal stem cells and in the positive regulation of neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells (By similarity). Promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells in the adult subventricular zone of the hippocampus by binding to and stabilizing SATB1 mRNA (By similarity). Binds and stabilizes MSI1 mRNA in neural stem cells (By similarity). Exhibits increased binding to ACHE mRNA during neuronal differentiation, thereby stabilizing ACHE mRNA and enhancing its expression (PubMed:12468554, PubMed:17234598). Protects CDKN1A mRNA from decay by binding to its 3'-UTR (By similarity). May bind to APP and BACE1 mRNAS and the BACE1AS lncRNA and enhance their stabilization (PubMed:24857657). Plays a role in neurite outgrowth and in the establishment and maturation of dendritic arbors, thereby contributing to neocortical and hippocampal circuitry function (By similarity). Stabilizes GAP43 mRNA and protects it from decay during postembryonic development in the brain (PubMed:12034726). By promoting the stabilization of GAP43 mRNA, plays a role in NGF-mediated neurite outgrowth (By similarity). Binds to BDNF long 3'UTR mRNA, thereby leading to its stabilization and increased dendritic translation after activation of PKC (By similarity). By increasing translation of BDNF after nerve injury, may contribute to nerve regeneration (By similarity). Acts as a stabilizing factor by binding to the 3'UTR of NOVA1 mRNA, thereby increasing its translation and enhancing its functional activity in neuron-specific splicing (PubMed:18218628). Stimulates translation of mRNA in a poly(A)- and cap-dependent manner, possibly by associating with the EIF4F cap-binding complex (By similarity). May also negatively regulate translation by binding to the 5'UTR of Ins2 mRNA, thereby repressing its translation (By similarity). Upon glucose stimulation, Ins2 mRNA is released from ELAVL4 and translational inhibition is abolished (By similarity). Also plays a role in the regulation of alternative splicing (PubMed:17035636). May regulate alternative splicing of CALCA pre-mRNA into Calcitonin and Calcitonin gene-related peptide 1 (CGRP) by competing with splicing regulator TIAR for binding to U-rich intronic sequences of CALCA pre- mRNA (PubMed:17035636). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Perikaryon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09032}. Cell projection, dendrite {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09032}. Cell projection, axon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61701}. Cell projection, growth cone {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61701}. Note=Co-localizes with ribosomal RNA in polysomes. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09032} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in pancreatic beta cells (at protein level) (PubMed:22387028). Expressed in the brain (PubMed:14702039, PubMed:1655278). |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.
¥ 1,500.00
Cat# AP54453























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。