KCNQ1 (7E1) Mouse mAb
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
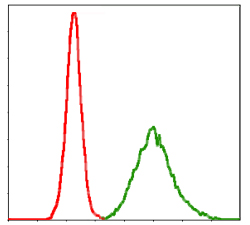
| WB, FC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P51787 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KCNQ1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Purification | Ascitic Fluid |
| Calculated MW | 74699 Da |
| Gene ID | 3784 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | LQT; RWS; WRS; LQT1; SQT2; ATFB1; ATFB3; JLNS1; KCNA8; KCNA9; Kv1.9; Kv7.1; KVLQT1; FLJ26167 |
| Dilution | WB~~1:3000 FC~~1:10~50 |
| Format | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Name | KCNQ1 (HGNC:6294) |
|---|---|
| Function | Pore-forming subunit of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel involved in the regulation of cardiomyocyte excitability and important in normal development and functions of myocardium, inner ear, stomach and colon (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:25441029). Associates with KCNE beta subunits that modulates current kinetics (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:19687231, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:9312006). Induces a voltage-dependent current by rapidly activating and slowly deactivating potassium-selective outward current (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:25441029, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:9312006). Also promotes a delayed voltage activated potassium current showing outward rectification characteristic (By similarity). During beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation, participates in cardiac repolarization by associating with KCNE1 to form the I(Ks) cardiac potassium current that increases the amplitude and slows down the activation kinetics of outward potassium current I(Ks) (By similarity) (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:9312006). Muscarinic agonist oxotremorine-M strongly suppresses KCNQ1/KCNE1 current (PubMed:10713961). When associated with KCNE3, forms the potassium channel that is important for cyclic AMP-stimulated intestinal secretion of chloride ions (PubMed:10646604). This interaction with KCNE3 is reduced by 17beta-estradiol, resulting in the reduction of currents (By similarity). During conditions of increased substrate load, maintains the driving force for proximal tubular and intestinal sodium ions absorption, gastric acid secretion, and cAMP-induced jejunal chloride ions secretion (By similarity). Allows the provision of potassium ions to the luminal membrane of the secretory canaliculus in the resting state as well as during stimulated acid secretion (By similarity). When associated with KCNE2, forms a heterooligomer complex leading to currents with an apparently instantaneous activation, a rapid deactivation process and a linear current-voltage relationship and decreases the amplitude of the outward current (PubMed:11101505). When associated with KCNE4, inhibits voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:19687231). When associated with KCNE5, this complex only conducts current upon strong and continued depolarization (PubMed:12324418). Also forms a heterotetramer with KCNQ5; has a voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:24855057). Binds with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PubMed:25037568). KCNQ1-KCNE2 channel associates with Na(+)-coupled myo-inositol symporter in the apical membrane of choroid plexus epithelium and regulates the myo- inositol gradient between blood and cerebrospinal fluid with an impact on neuron excitability (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane Early endosome. Membrane raft. Endoplasmic reticulum Basolateral cell membrane. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97414}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Colocalized with KCNE3 at the plasma membrane (PubMed:10646604). Upon 17beta-oestradiol treatment, colocalizes with RAB5A at early endosome (PubMed:23529131). Heterotetramer with KCNQ5 is highly retained at the endoplasmic reticulum and is localized outside of lipid raft microdomains (PubMed:24855057). During the early stages of epithelial cell polarization induced by the calcium switch, it is removed from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is retained, and redistributed to the basolateral cell surface in a PI3K-dependent manner at a later stage (PubMed:21228319). Colocalizes with SLC5A3 at the apical membrane of choroid plexus epithelium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10646604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21228319, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23529131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24855057} |
| Tissue Location | Abundantly expressed in heart, pancreas, prostate, kidney, small intestine and peripheral blood leukocytes. Less abundant in placenta, lung, spleen, colon, thymus, testis and ovaries |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Swiss-Prot Acc.P51787.This gene encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel required for repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. This protein can form heteromultimers with two other potassium channel proteins, KCNE1 and KCNE3. Mutations in this gene are associated with hereditary long QT syndrome 1 (also known as Romano-Ward syndrome), Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, and familial atrial fibrillation. This gene exhibits tissue-specific imprinting, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in some tissues, and biallelic expression in others. This gene is located in a region of chromosome 11 amongst other imprinted genes that are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), and itself has been shown to be disrupted by chromosomal rearrangements in patients with BWS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。