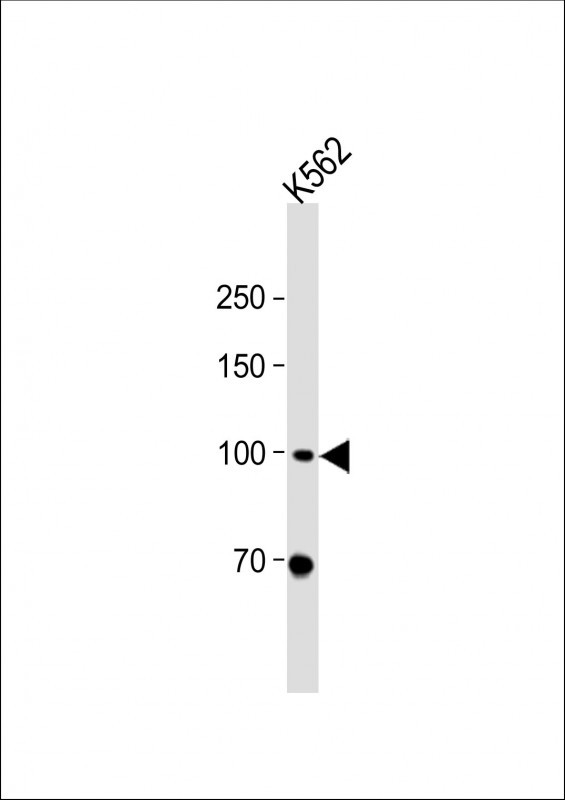
MLL5 Antibody (N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 2
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8IZD2 |
| Other Accession | Q3UG20, Q8NFF8, NP_891847.1, NP_061152.3 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 204965 Da |
| Antigen Region | 93-120 aa |
| Gene ID | 55904 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2E, Lysine N-methyltransferase 2E, Myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia protein 5, KMT2E, MLL5 |
| Target/Specificity | This MLL5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 93-120 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human MLL5. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.05% (V/V) Proclin 300. This antibody is prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) precipitation followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | MLL5 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | KMT2E |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MLL5 |
| Function | Associates with chromatin regions downstream of transcriptional start sites of active genes and thus regulates gene transcription (PubMed:23629655, PubMed:23798402, PubMed:24130829). Chromatin interaction is mediated via the binding to tri-methylated histone H3 at 'Lys-4' (H3K4me3) (PubMed:23798402, PubMed:24130829). Key regulator of hematopoiesis involved in terminal myeloid differentiation and in the regulation of hematopoietic stem cell (HSCs) self-renewal by a mechanism that involves DNA methylation (By similarity). Also acts as an important cell cycle regulator, participating in cell cycle regulatory network machinery at multiple cell cycle stages including G1/S transition, S phase progression and mitotic entry (PubMed:14718661, PubMed:18573682, PubMed:19264965, PubMed:23629655). Recruited to E2F1 responsive promoters by HCFC1 where it stimulates tri-methylation of histone H3 at 'Lys-4' and transcriptional activation and thereby facilitates G1 to S phase transition (PubMed:23629655). During myoblast differentiation, required to suppress inappropriate expression of S-phase-promoting genes and maintain expression of determination genes in quiescent cells (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Chromosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Nucleus speckle. Note=Absent from the nucleolus (PubMed:14718661). Localizes to chromosome during interphase and to centrosomes during mitosis (PubMed:23798402). Dissociation from mitotic chromosome is likely due to histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Thr-3' and 'Thr-6' (PubMed:23798402). [Isoform NKp44L]: Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed in both adult and fetal tissues (PubMed:12101424, PubMed:23958951). Highest levels of expression observed in fetal thymus and kidney and in adult hematopoietic tissues, jejunum and cerebellum (PubMed:12101424, PubMed:23958951). Isoform NKp44L: Not detected on circulating cells from healthy individuals, but is expressed on a large panel of tumor and transformed cells (PubMed:23958951). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene is a member of the myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) family and encodes a protein with an N-terminal PHD zinc finger and a central SET domain. Overexpression of the protein inhibits cell cycle progression. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq].
REFERENCES
Liu, J., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 285(27):20904-20914(2010)
Fujiki, R., et al. Nature 459(7245):455-459(2009)
Cheng, F., et al. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 40(11):2472-2481(2008)
Sun, X.J., et al. PLoS ONE 3 (1), E1499 (2008) :
Olsen, J.V., et al. Cell 127(3):635-648(2006)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。