CCNE1 Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
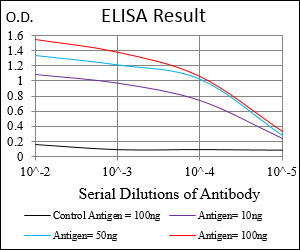
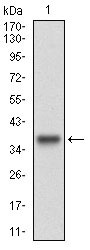
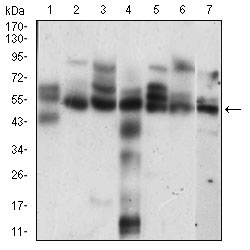
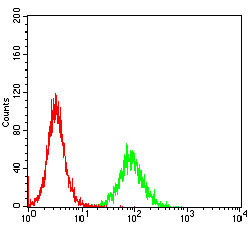
Application
| WB, FC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P24864 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 5F8C5 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Calculated MW | 47077 Da |
| Description | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK2, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein accumulates at the G1-S phase boundary and is degraded as cells progress through S phase. Overexpression of this gene has been observed in many tumors, which results in chromosome instability, and thus may contribute to tumorigenesis. This protein was found to associate with, and be involved in, the phosphorylation of NPAT protein (nuclear protein mapped to the ATM locus), which participates in cell-cycle regulated histone gene expression and plays a critical role in promoting cell-cycle progression in the absence of pRB. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct isoforms, have been described. Two additional splice variants were reported but detailed nucleotide sequence information is not yet available. |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CCNE1 (AA: 307-410) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
| Gene ID | 898 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | G1/S-specific cyclin-E1, CCNE1, CCNE |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500 - 1/2000 FC~~1/200 - 1/400 E~~1/10000 |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CCNE1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CCNE1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CCNE |
| Function | Essential for the control of the cell cycle at the G1/S (start) transition. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in testis and placenta. Low levels in bronchial epithelial cells. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
C17orf53 (chromosome 17 open reading frame 53) is a 647 amino acid protein that is encoded by a gene mapping to human chromosome 17. Chromosome 17 makes up over 2.5% of the human genome with about 81 million bases encoding over 1,200 genes. Two key tumor suppressor genes are associated with chromosome 17, namely, p53 and BRCA1. Tumor suppressor p53 is necessary for maintenance of cellular genetic integrity by moderating cell fate through DNA repair versus cell death. Malfunction or loss of p53 expression is associated with malignant cell growth and Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Like p53, BRCA1 is directly involved in DNA repair, specifically it is recognized as a genetic determinant of early onset breast cancer and predisposition to cancers of the ovary, colon, prostate gland and fallopian tubes. Chromosome 17 is also linked to neurofibromatosis, a condition characterized by neural and epidermal lesions, and dysregulated Schwann cell growth. Alexander disease, Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome and Canavan disease are also associated with chromosome 17. ; ;
REFERENCES
1. Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;70(12):5074-84. 2. Cancer. 2010 Jun 1;116(11):2621-34.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。