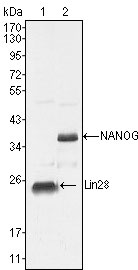
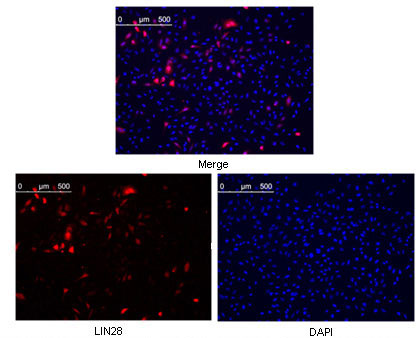
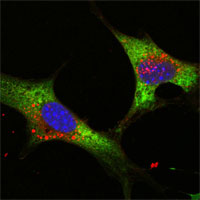
LIN28 Antibody
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H9Z2 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 6D1F9 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Calculated MW | 22743 Da |
| Description | LIN28: lin-28 homolog (C. elegans), also known as CSDD1, ZCCHC1. Entrez Protein NP_078950. LIN28 was first discovered in the nematode C. elegans. It is a heterochronic protein in C. elegans involved in the timing of developmental events and choice of stage specific cell fates. LIN28 expression has been found to be regulated post-transcriptionally by miRNAs in both nematodes and mammals. In humans it is expressed in embryonic stem cells and its expression decreases during differentiation. It is negatively regulated by retinoic acid in neuronal differentiation. |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of LIN28 (aa93-209) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Antibody are purified by protein G affinity chromatography. Liquid in 0.01M Phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
| Gene ID | 79727 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Protein lin-28 homolog A, Lin-28A, Zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 1, LIN28A, CSDD1, LIN28, ZCCHC1 |
| Dilution | WB~~1/500 - 1/2000 ICC~~N/A E~~N/A |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | LIN28 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | LIN28A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CSDD1, LIN28, ZCCHC1 |
| Function | RNA-binding protein that inhibits processing of pre-let-7 miRNAs and regulates translation of mRNAs that control developmental timing, pluripotency and metabolism (PubMed:21247876). Seems to recognize a common structural G-quartet (G4) feature in its miRNA and mRNA targets (Probable). 'Translational enhancer' that drives specific mRNAs to polysomes and increases the efficiency of protein synthesis. Its association with the translational machinery and target mRNAs results in an increased number of initiation events per molecule of mRNA and, indirectly, in mRNA stabilization. Binds IGF2 mRNA, MYOD1 mRNA, ARBP/36B4 ribosomal protein mRNA and its own mRNA. Essential for skeletal muscle differentiation program through the translational up- regulation of IGF2 expression. Suppressor of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis, including that of let-7, miR107, miR-143 and miR-200c. Specifically binds the miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs), recognizing an 5'-GGAG-3' motif found in pre-miRNA terminal loop, and recruits TUT4 and TUT7 uridylyltransferases (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). This results in the terminal uridylation of target pre-miRNAs (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). Uridylated pre-miRNAs fail to be processed by Dicer and undergo degradation. The repression of let-7 expression is required for normal development and contributes to maintain the pluripotent state by preventing let-7-mediated differentiation of embryonic stem cells (PubMed:18951094, PubMed:19703396, PubMed:22118463, PubMed:22898984). Localized to the periendoplasmic reticulum area, binds to a large number of spliced mRNAs and inhibits the translation of mRNAs destined for the ER, reducing the synthesis of transmembrane proteins, ER or Golgi lumen proteins, and secretory proteins. Binds to and enhances the translation of mRNAs for several metabolic enzymes, such as PFKP, PDHA1 or SDHA, increasing glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. Which, with the let-7 repression may enhance tissue repair in adult tissue (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Rough endoplasmic reticulum {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3}. Cytoplasm, P-body. Cytoplasm, Stress granule. Nucleus, nucleolus {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3}. Note=Predominantly cytoplasmic (PubMed:22118463). In the cytoplasm, localizes to peri-endoplasmic reticulum regions and detected in the microsomal fraction derived from rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) following subcellular fractionation May be bound to the cytosolic surface of RER on which ER-associated mRNAs are translated (By similarity). Shuttle from the nucleus to the cytoplasm requires RNA-binding (PubMed:17617744). Nucleolar localization is observed in 10-15% of the nuclei in differentiated myotubes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3Y3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17617744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22118463} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in embryonic stem cells, placenta and testis. Tends to be up-regulated in HER2-overexpressing breast tumors |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
1. Dev Dyn. 2005 Feb;232(2):487-97. 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(21):9198-208.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。