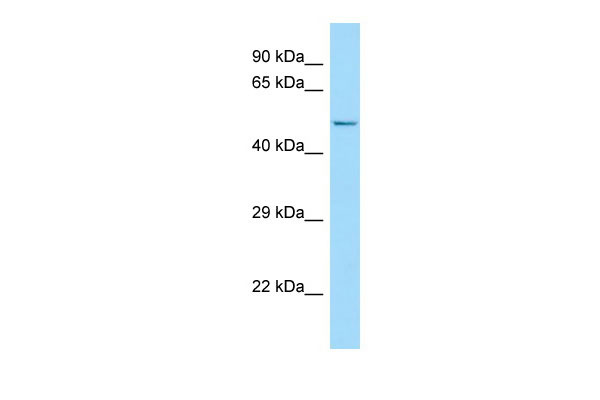
FLVCR2 Antibody - C-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UPI3 |
| Other Accession | NM_017791, NP_060261 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Pig, Dog, Guinea Pig, Horse, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 57241 Da |
| Gene ID | 55640 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | C14orf58, CCT, FLJ20371, FLVCRL14q, EPV, PVHH, MFSD7C |
| Other Names | Feline leukemia virus subgroup C receptor-related protein 2, Calcium-chelate transporter, CCT, FLVCR2, C14orf58 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 50 ul of distilled water. Final anti-FLVCR2 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FLVCR2 Antibody - C-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FLVCR2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:20823265, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:20105} |
|---|---|
| Function | Choline uniporter that specifically mediates choline uptake at the blood-brain-barrier (PubMed:38302740, PubMed:38778100). Responsible for the majority of choline uptake across the blood-brain- barrier from the circulation into the brain (By similarity). Choline, a nutrient critical for brain development, is a precursor of phosphatidylcholine, as well as betaine (By similarity). Also mediates transport of ethanolamine (PubMed:38778100). Choline and ethanolamine transport is not coupled with proton transport and is exclusively driven by the choline gradient across the plasma membrane (PubMed:38778100). However, the presence of an inwardly directed proton gradient enhances choline uptake (By similarity). Also acts as a heme b transporter (PubMed:20823265, PubMed:32973183). Required to regulate mitochondrial respiration processes, ATP synthesis and thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). At low heme levels, interacts with components of electron transfer chain (ETC) complexes and ATP2A2, leading to ubiquitin-mediated degradation of ATP2A2 and inhibition of thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). Upon heme binding, dissociates from ETC complexes to allow switching from mitochondrial ATP synthesis to thermogenesis (PubMed:32973183). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Mitochondrion membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Present on both luminal (blood-facing) and abluminal (brain-facing) sides of brain endothelial cell plasma membranes, with higher luminal membrane expression (By similarity) Also localizes in mitochondria where it interacts with components of the electron transfer complexes III, IV and V (PubMed:32973183) Colocalizes with ATP2A2 at the mitochondrial-ER contact junction (PubMed:32973183). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91X85, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32973183} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in non-hematopoietic tissues, with relative abundant expression in brain, placenta, lung, liver and kidney (PubMed:20823265). Also expressed in hematopoietic tissues (fetal liver, spleen, lymph node, thymus, leukocytes and bone marrow) (PubMed:20823265). Found in acidophil cells of the pituitary that secrete growth hormone and prolactin (at protein level) (PubMed:14729055). |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
REFERENCES
Brasier G.,et al.Exp. Cell Res. 293:31-42(2004).
Brown J.,et al.Submitted (DEC-2001) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Heilig R.,et al.Nature 421:601-607(2003).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (JUL-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。