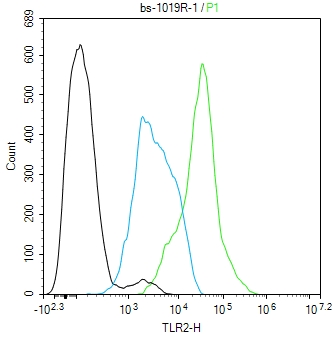
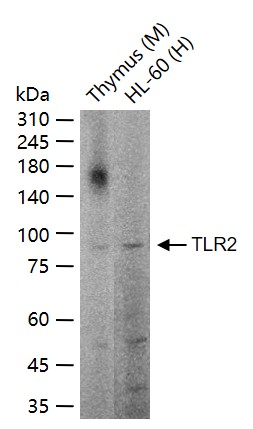
TLR2 Rabbit pAb
TLR2 Rabbit pAb
- 产品详情
- 文献引用 : 1
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O60603 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 89838 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human TLR2 |
| Epitope Specificity | 701-784/784 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the Toll-like receptor family.Contains 14 LRR (leucine-rich) repeats.Contains 1 TIR domain. |
| SUBUNIT | Interacts with LY96, TLR1 and TLR6 (via extracellular domain). Binds MYD88 (via TIR domain). Interacts with TICAM1. Ligand binding induces the formation of a heterodimer with TLR1. Interacts with CNPY3. |
| Post-translational modifications | Glycosylation of Asn-442 is critical for secretion of the N-terminal ectodomain of TLR2. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This gene is expressed most abundantly in peripheral blood leukocytes, and mediates host response to Gram-positive bacteria and yeast via stimulation of NF-kappaB. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
| Gene ID | 7097 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Toll-like receptor 2, Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 4, CD282, TLR2 (HGNC:11848), TIL4 |
| Target/Specificity | Highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, in particular in monocytes, in bone marrow, lymph node and in spleen. Also detected in lung and in fetal liver. Levels are low in other tissues. |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,Flow-Cyt=1 µg/Test |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | TLR2 (HGNC:11848) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | TIL4 |
| Function | Cooperates with LY96 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins and other microbial cell wall components. Cooperates with TLR1 or TLR6 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides (PubMed:17889651, PubMed:21078852). Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. May also activate immune cells and promote apoptosis in response to the lipid moiety of lipoproteins (PubMed:10426995, PubMed:10426996). Recognizes mycoplasmal macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2kD (MALP-2), soluble tuberculosis factor (STF), phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) and B.burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein (OspA-L) cooperatively with TLR6 (PubMed:11441107). Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M.tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via this receptor, but also partially via TLR4 (PubMed:16622205). MAPK activation in response to bacterial peptidoglycan also occurs via this receptor (PubMed:16622205). Acts as a receptor for M.tuberculosis lipoproteins LprA, LprG, LpqH and PstS1, some lipoproteins are dependent on other coreceptors (TLR1, CD14 and/or CD36); the lipoproteins act as agonists to modulate antigen presenting cell functions in response to the pathogen (PubMed:19362712). M.tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) but not HSP65 (groEL-2) acts via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression (PubMed:15809303). Recognizes M.tuberculosis major T-antigen EsxA (ESAT-6) which inhibits downstream MYD88-dependent signaling (shown in mouse) (By similarity). Forms activation clusters composed of several receptors depending on the ligand, these clusters trigger signaling from the cell surface and subsequently are targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway. Forms the cluster TLR2:TLR6:CD14:CD36 in response to diacylated lipopeptides and TLR2:TLR1:CD14 in response to triacylated lipopeptides (PubMed:16880211). Required for normal uptake of M.tuberculosis, a process that is inhibited by M.tuberculosis LppM (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QUN7}; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, phagosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QUN7}; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane raft. Note=Does not reside in lipid rafts before stimulation but accumulates increasingly in the raft upon the presence of the microbial ligand. In response to diacylated lipoproteins, TLR2:TLR6 heterodimers are recruited in lipid rafts, this recruitment determines the intracellular targeting to the Golgi apparatus. Triacylated lipoproteins induce the same mechanism for TLR2:TLR1 heterodimers. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, in particular in monocytes, in bone marrow, lymph node and in spleen. Also detected in lung and in fetal liver. Levels are low in other tissues |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This gene is expressed most abundantly in peripheral blood leukocytes, and mediates host response to Gram-positive bacteria and yeast via stimulation of NF-kappaB. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008].
REFERENCES
Chaudhary P.M.,et al.Blood 91:4020-4027(1998).
Rock F.L.,et al.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95:588-593(1998).
Yang R.-B.,et al.Nature 395:284-288(1998).
Nakajima T.,et al.Immunogenetics 60:727-735(2008).
Georgel P.,et al.PLoS ONE 4:E7803-E7803(2009).
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。